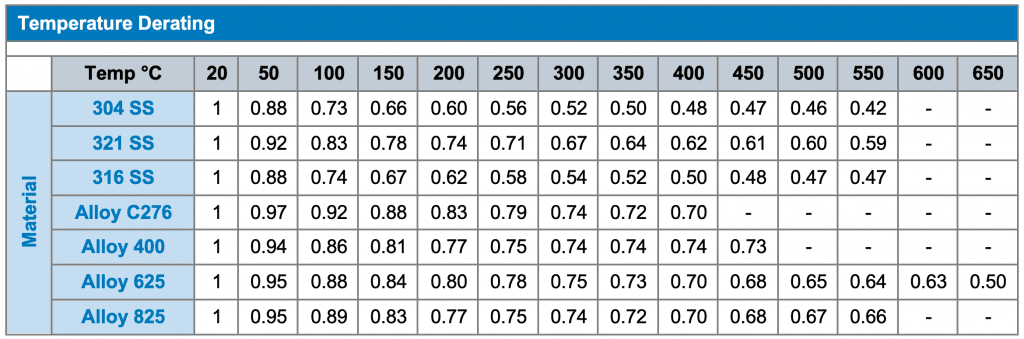
In the metallic hose world, this means that the Maximum Working Pressure (MWP) of a metallic hose must be reduced or “derated” as operating temperature increases.
The degree of strength reduction is predictable, so it is relatively straightforward to determine the combination of temperature and pressure that can be accommodated by a metallic hose.
Some metals are better than others in this respect, so in a particularly demanding application with a combination of sustained high temperature and high pressure, it is often possible to select a more exotic alloy that will meet the demand.
The table below enables easy selection of the correct derating factor for each alloy through a range of temperatures. This table is based on data from ISO 10380:2012.